Transmission
modes
· The way in which data is transmitted from one device to another device is known as transmission mode.
· The transmission mode is also known as the communication mode.
· Each communication channel has a direction associated with it, and transmission media provide the direction. Therefore, the transmission mode is also known as a directional mode.
· The transmission mode is defined in the physical layer.
The Transmission mode
is divided into three categories:
·
Simplex
mode
·
Half-duplex
mode
·
Full-duplex
mode
1. Simplex Mode
- In Simplex mode, the communication is
unidirectional, i.e., the data flow in one direction.
- A device can only send the data but
cannot receive it or it can receive the data but cannot send the data.
- This transmission mode is not very
popular as mainly communications require the two-way exchange of data. The
simplex mode is used in the business field as in sales that do not require
any corresponding reply.
- The radio station is a simplex channel as
it transmits the signal to the listeners but never allows them to transmit
back.
- Keyboard and Monitor are the examples of
the simplex mode as a keyboard can only accept the data from the user and
monitor can only be used to display the data on the screen.
- The main advantage of the simplex mode is
that the full capacity of the communication channel can be utilized during
transmission.
- In
simplex mode, the station can utilize the entire bandwidth of the
communication channel, so that more data can be transmitted at a time.
- Communication
is unidirectional, so it has no inter-communication between devices.
- Communication
is unidirectional, so it has no inter-communication between devices.
- In a
Half-duplex channel, direction can be reversed, i.e., the station can
transmit and receive the data as well.
- Messages
flow in both the directions, but not at the same time.
- The
entire bandwidth of the communication channel is utilized in one direction
at a time.
- In
half-duplex mode, it is possible to perform the error detection, and if
any error occurs, then the receiver requests the sender to retransmit the
data.
- A Walkie-talkie is
an example of the Half-duplex mode. In Walkie-talkie, one party speaks,
and another party listens. After a pause, the other speaks and first party
listens. Speaking simultaneously will create the distorted sound which
cannot be understood.
Advantage of Half-duplex mode:
- In
half-duplex mode, both the devices can send and receive the data and also
can utilize the entire bandwidth of the communication channel during the
transmission of data.
Disadvantage of Half-Duplex mode:
- In half-duplex mode, when one device is sending the data, then another has to wait, this causes the delay in sending the data at the right time.
- In
Full duplex mode, the communication is bi-directional, i.e., the data flow
in both the directions.
- Both
the stations can send and receive the message simultaneously.
- Full-duplex
mode has two simplex channels. One channel has traffic moving in one
direction, and another channel has traffic flowing in the opposite
direction.
- The
Full-duplex mode is the fastest mode of communication between devices.
- The
most common example of the full-duplex mode is a telephone network. When
two people are communicating with each other by a telephone line, both can
talk and listen at the same time.
Advantage of Full-duplex mode:
- Both
the stations can send and receive the data at the same time.
Disadvantage of Full-duplex mode:
- If
there is no dedicated path exists between the devices, then the capacity
of the communication channel is divided into two parts.
Types of Transmission
·
Synchronous
Transmission
·
Asynchronous
Transmission
Synchronous Transmission:
In synchronous transmission, when sender is
sending the data, receiver is ready to receive the data at the same time. In Synchronous
Transmission, data is sent in form of blocks or frames. This transmission is
the full duplex type. Between sender and receiver the synchronization is
compulsory. In Synchronous transmission, There is no gap present between data.
It is more efficient and more reliable than asynchronous transmission to
transfer the large amount of data.
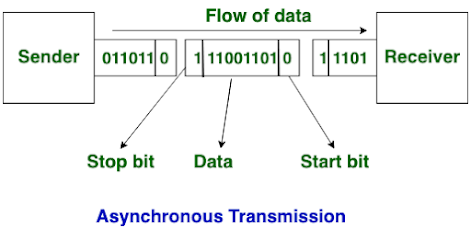
Asynchronous Transmission:
In Asynchronous Transmission, data is sent in form of byte or character. This
transmission is the half duplex type transmission. In this transmission start
bits and stop bits are added with data. It does not require synchronization.
Now,
let’s see the difference between Synchronous and Asynchronous Transmission:
|
S.NO |
Synchronous Transmission |
Asynchronous Transmission |
|
1. |
In Synchronous transmission, Data
is sent in form of blocks or frames. |
In asynchronous transmission, Data
is sent in form of byte or character. |
|
2. |
Synchronous transmission is fast. |
Asynchronous transmission is slow. |
|
3. |
Synchronous transmission is
costly. |
Asynchronous transmission is
economical. |
|
4. |
In Synchronous transmission, time
interval of transmission is constant. |
In asynchronous transmission, time
interval of transmission is not constant, it is random. |
|
5. |
In Synchronous transmission, There
is no gap present between data. |
In asynchronous transmission,
There is present gap between data. |
|
6. |
Efficient use of transmission line
is done in synchronous transmission. |
While in asynchronous
transmission, transmission line remains empty during gap in character
transmission. |
|
7. |
Synchronous transmission needs
precisely synchronized clocks for the information of new bytes. |
Asynchronous transmission have no
need of synchronized clocks as parity bit is used in this transmission for
information of new bytes. |